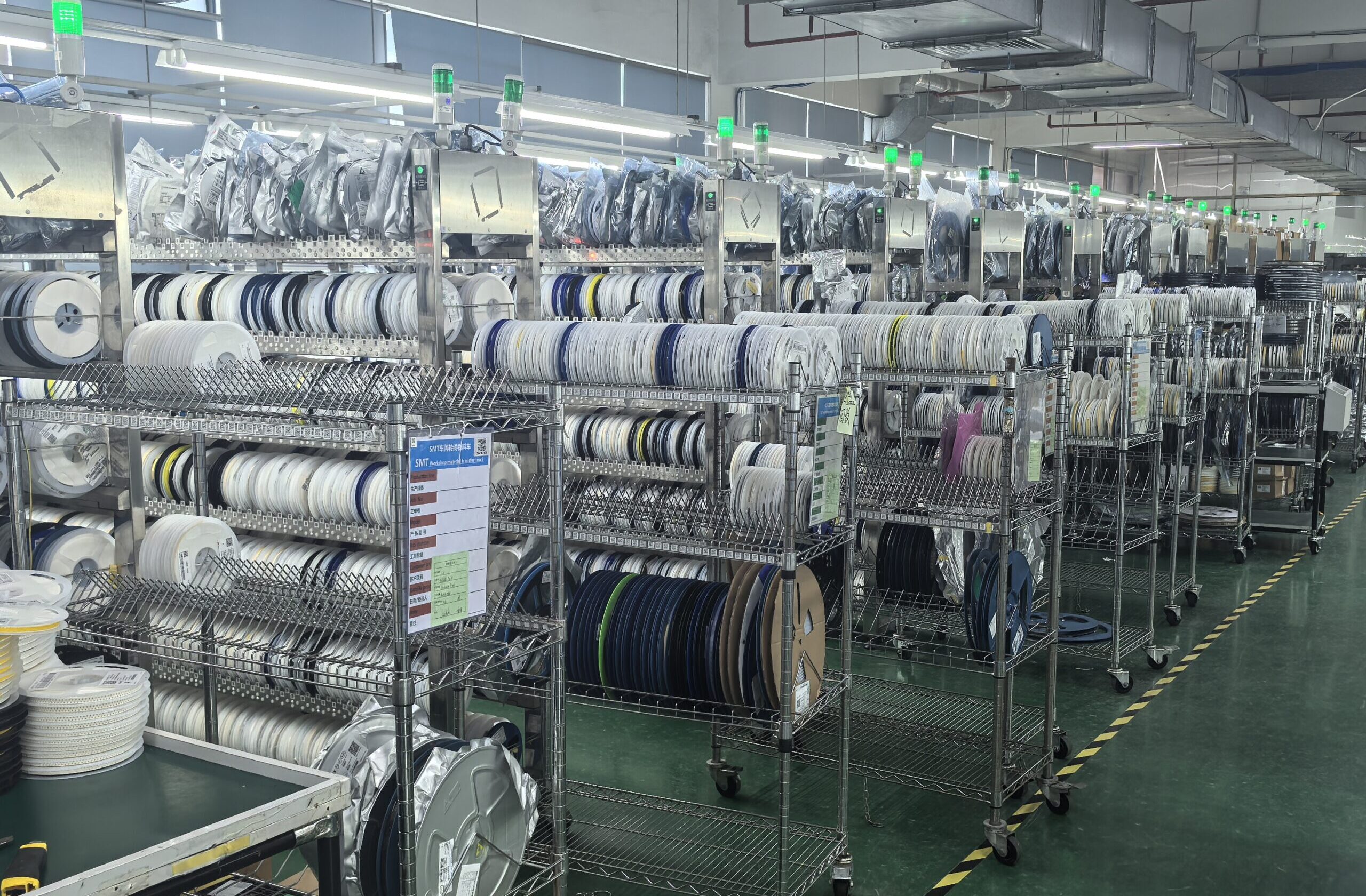
SMT Chip Processing Manufacturer
Chip processing using SMT (surface mount technology) is a method of producing electronic components and circuit boards. It entails using a pick-and-place machine to place small surface mount devices (SMDs) onto a printed circuit board (PCB). SMDs are typically made of a metal and plastic blend, and they have tiny leads or pads that are soldered to the PCB.
Committed to Manufacturing Solutions
Surface mount technology (SMT) is an assembly and production method that applies electronic components directly onto the surface of a printed circuit board (PCB). This process allows for automated production to complete more of the required assembly to create a working board.




We can provide to...
- Turn times as short as 24 hours
- 1 to 100,000 units
- Class II Inspection standard and Class III Inspection available
- 100% on-time guarantee
- DFM support
- Lead free (RoHS) options
- SMT and thru-hole capabilities
- All SMT machine placed
- AOI (Automated Optical Inspection)
- Lead-free RoHS Certification and ITAR compliance screen available
-
Program Design
-
Assembly Capacity
-
SMT Capacity
-
Equipment Exhibition
From element procurement to functional testing and package completion, we offer a one-stop shop for all types of PCBs.
Assembly Capacity
| Turn-key | Purchase from authorized suppliers, distributors |
| Consigned | Accept parts in reels, cut tapes, tubes & pallets and bulk. |
| Stencils | Offer Laser-cut stainless steel stencil. |
| Solder type | Offer both lead&lead-freeassembly services. |
| Board type | Rigid board, flex board&rigid-flex board. |
| PCB or Panel Size | Min board size of 10*10mm |
| PCB or Panel Size | Max board size of 330*530. |
| Assemble type | The customer provides some components |
| Board shape | There is no limit to shape |
| Prototype | MOQ as low to 5units in 1-2 days delivery |
| Low volume | Offer 3-4 days quick turn time service for low volume. |
| High volumn | Offer accurate delivery to catch your deadline. |
SMT Capacity
| Single and double sided SMT/PTH | Yes |
| Large parts on both sides | Yes |
| BGA on both sides | Yes |
| Smallest Chips size | 201 |
| Min BGA | 0.008 in. (0.2mm) pitch |
| Micro BGA pitch | ball count greater than 1000 |
| Min Leaded parts pitch | 0.008 in. (0.2 mm) |
| Max Parts size | 2.2 in. x 2.2 in. x 0.6 in. |
| Odd form parts: | Yes,Assembly by hands |
| LED | Yes,Assembly by hands |
| Wave soldering | Yes |
| Max PCB size | 14.5 in. x 19.5 in. |
| Min PCB Thickness | 0.02 |
| Fiducial Marks | Preferred but not required |
| PCB Finish: | SMOBC/HASL |
| PCB Finish: | Electrolytic gold |
| PCB Finish: | Electroless gold |
| PCB Finish: | Electroless silver |
| Ball counts | ball count greater than 1000 |
| Resistor | Yes,Assembly by hands |
| Capacitor networks | Yes,Assembly by hands |
| Electrolytic capacitors | Yes,Assembly by hands |
| Variable resistors、capacitors (pots) | Yes,Assembly by hands |
| Sockets | Yes,Assembly by hands |
| PCB Shape | Any |
| Panelized PCB | Tab routed |
| Panelized PCB | Breakaway tabs |
| Panelized PCB | V-Scored |
| Panelized PCB | Routed+ V scored |
| Inspection | X-ray analysis |
| Inspection | Microscope to 20X |
| Rework | BGA removal and replacement station |
| PCB Finish: | Immersion gold |
| PCB Finish: | Immersion tin |
| PCB Finish: | OSP |
PCB Products show
SMD Placement and Soldering Process
The pick-and-place machine takes SMDs from a reel or tray with a vacuum nozzle and places them on the PCB according to a set of instructions known as a pick-and-place file. A small amount of adhesive or their weight holds the SMDs in place on the PCB.
Following the placement of the SMDs on the PCB, the board is typically reflow soldered, which involves heating the board to a high temperature to melt the solder and create a permanent connection between the SMDs and the PCB. The board is then cooled, and any excess solder is removed using a technique known as solder paste cleaning.


Bring you better PCB products
Circuit Board Fabrication and PCB Assembly Turnkey Services
SMT Chip Processing asked questions
What is SMT chip processing?
How is SMT chip processing different from through-hole technology?
What are the advantages of SMT chip processing?
What are the challenges of SMT chip processing?
What equipment is used in SMT chip processing?
What is the process of SMT chip processing?
Preparation: The PCB is cleaned and prepared for the soldering process.
Printing: Solder paste is applied to the PCB using a solder paste stencil.
Placement: The pick and place machine places the components onto the PCB in the correct positions.
Reflow: The PCB and components are placed in a reflow oven, where they are heated to a high temperature, melting the solder and causing it to flow around the components.
Inspection: The completed PCB is inspected to ensure that all components are correctly placed and soldered.
What are some common defects in SMT chip processing
Why Choose Us?
WINOW has been providing high-quality PCBs with fast turnaround times and high customer satisfaction since 2018. We are one of China's largest and most skilled board manufacturers.
-
Orders for prototypes are processed within 24 hours.
-
PCB prototypes and small-batch manufacturing typically take 5-7 working days.
-
Small batch production and some PCB prototypes have a 48-hour lead time.




