ICT (In-Circuit Test)
In-circuit test (ICT) is a method of testing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic components to ensure that they are functioning correctly and meet specified quality standards. It is commonly used in the electronics manufacturing industry to identify and correct defects before the final product is assembled.
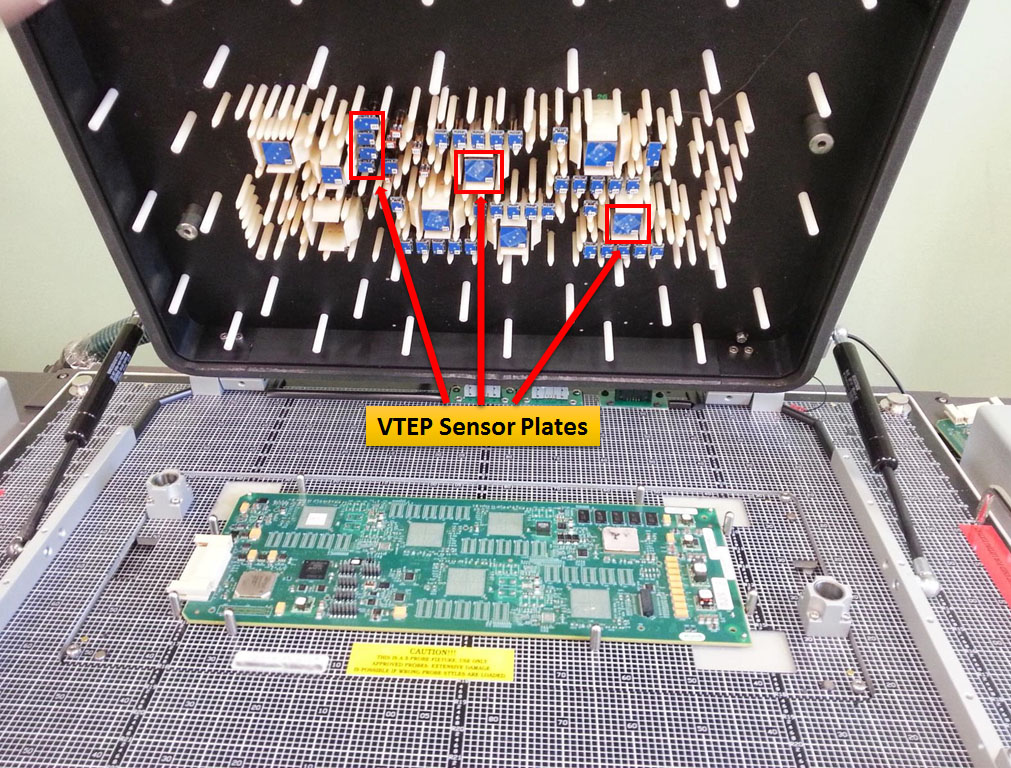
In ICT, a specialized testing machine is used to send electrical signals through the PCB or component and measure the responses. The testing machine is programmed with the expected responses for each signal, and any deviations from the expected response are flagged as defects.
There are several benefits to using ICT:
- High speed and accuracy: ICT can quickly and accurately identify defects, reducing the need for manual testing and increasing the speed of the manufacturing process.
- Increased defect detection: ICT can detect defects that may be difficult or impossible for a human tester to see, such as shorts or opens in circuit traces.
- Reduced testing costs: Automated testing reduces the need for manual labor, which can significantly reduce testing costs.
- Improved product quality: By identifying and correcting defects early in the manufacturing process, ICT can help improve the overall quality of the finished product.
However, there are also some limitations to ICT:
- Cost: ICT equipment can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Limited to surface inspection: ICT is typically limited to testing the surface of the PCB or component, and may not be able to detect internal defects.
- Dependence on test program: The accuracy of the test results depends on the accuracy of the test program, which must be carefully developed and maintained.
- Limited to functional testing: ICT is typically limited to functional testing, and may not be able to detect physical defects such as scratches or dents.
ICT (In-Circuit Test) FAQ
- What is in-circuit test (ICT)?
In-circuit test (ICT) is a method of testing printed circuit boards (PCBs) and other electronic components to ensure that they are functioning correctly and meet specified quality standards. It is commonly used in the electronics manufacturing industry to identify and correct defects before the final product is assembled.
- How does ICT work?
In ICT, a specialized testing machine is used to send electrical signals through the PCB or component and measure the responses. The testing machine is programmed with the expected responses for each signal, and any deviations from the expected response are flagged as defects.
- What are the benefits of ICT?
There are several benefits to using ICT:
- High speed and accuracy: ICT can quickly and accurately identify defects, reducing the need for manual testing and increasing the speed of the manufacturing process.
- Increased defect detection: ICT can detect defects that may be difficult or impossible for a human tester to see, such as shorts or opens in circuit traces.
- Reduced testing costs: Automated testing reduces the need for manual labor, which can significantly reduce testing costs.
- Improved product quality: By identifying and correcting defects early in the manufacturing process, ICT can help improve the overall quality of the finished product.
- What are the limitations of ICT?
There are a few limitations to ICT:
- Cost: ICT equipment can be expensive to purchase and maintain.
- Limited to surface inspection: ICT is typically limited to testing the surface of the PCB or component, and may not be able to detect internal defects.
- Dependence on test program: The accuracy of the test results depends on the accuracy of the test program, which must be carefully developed and maintained.
- Limited to functional testing: ICT is typically limited to functional testing, and may not be able to detect physical defects such as scratches or dents.
- What types of products can be tested with ICT?
ICT can be used to test a wide range of electronic components, including PCBs, microelectronic devices, and other electronic components. It is commonly used in the electronics manufacturing industry to test components before they are assembled into final products.

